Designing an Effective Cryogenic NRU
Designing a Nitrogen Rejection Unit (NRU) requires careful consideration of process conditions, equipment selection, and operational flexibility. Cryogenic distillation, the most effective method for nitrogen removal, involves complex design choices that impact performance and cost. This blog outlines key design concepts for cryogenic NRUs, focusing on column configuration, heat exchangers, and reflux systems.
Core Design Concepts for Cryogenic NRU
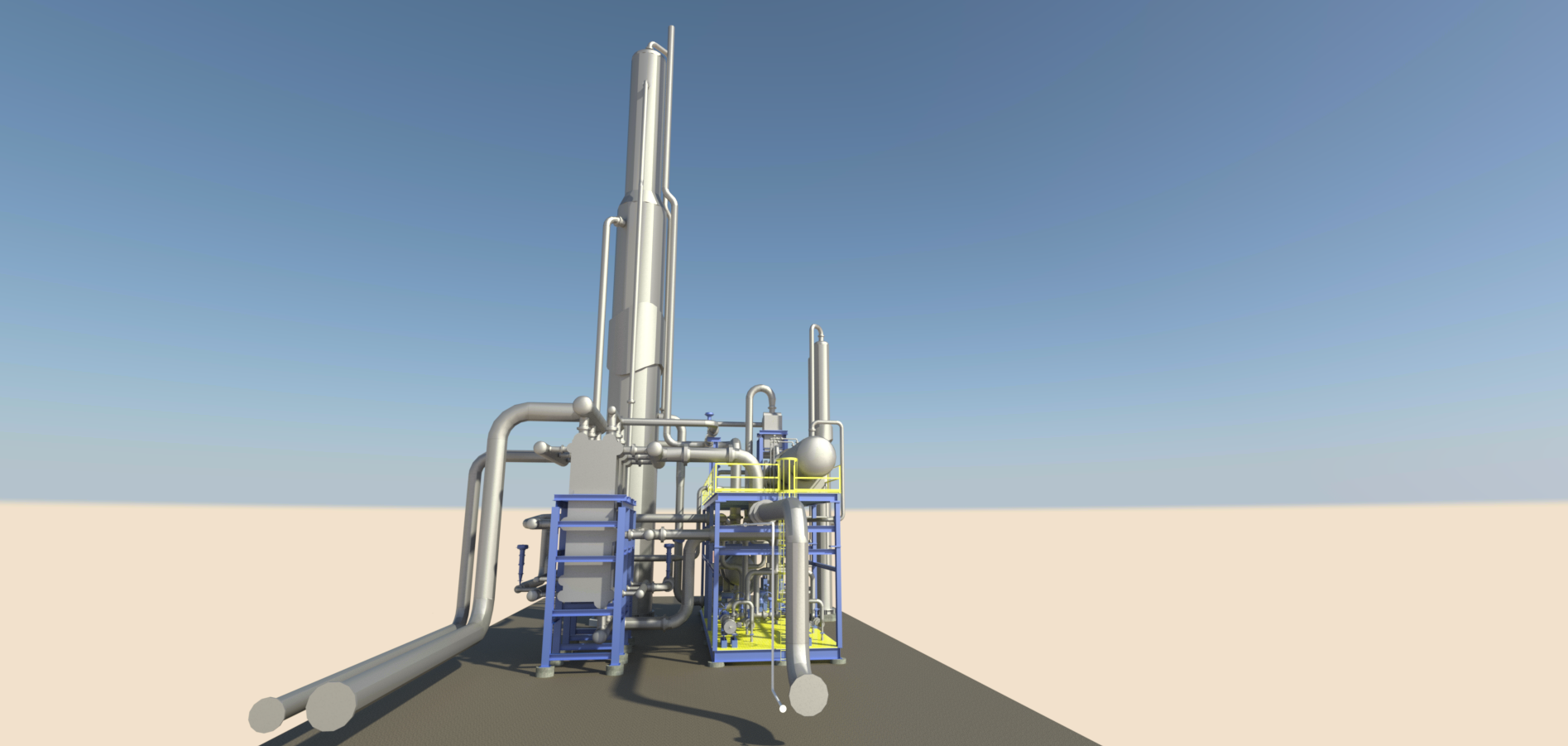
- Single vs. Dual Column Systems:
- Single Column: Best for high nitrogen content (>25 mol%) or low-capacity operations prioritizing simplicity and cost. It offers reliable performance with lower upfront costs.
- Dual Column: Ideal for lower nitrogen content (<25 mol%) where efficiency and power savings are critical. Though more complex, it reduces compression needs, lowering long-term costs.
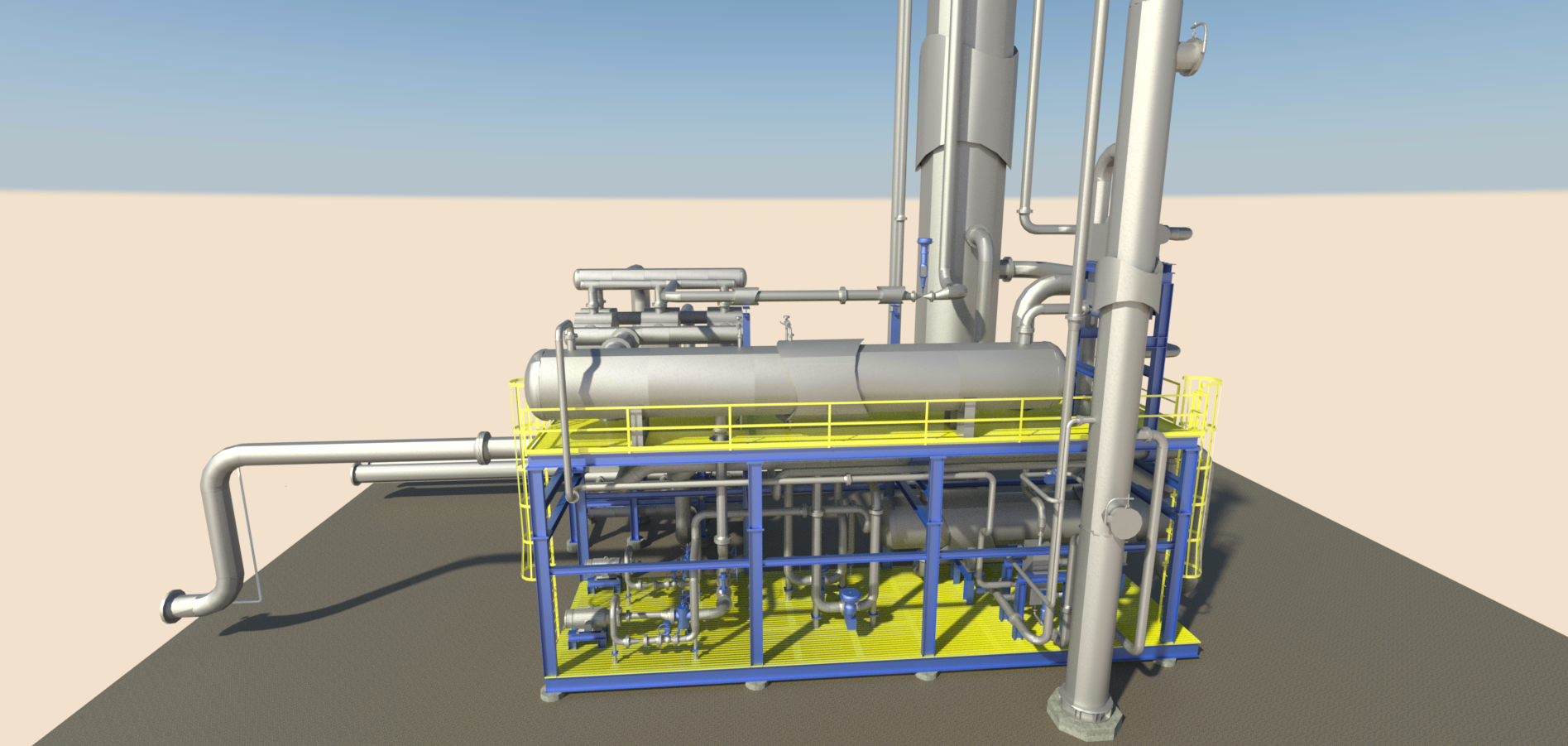
- Brazed Aluminum Heat Exchangers (BAHE):
- Highly efficient and compact, BAHEs are standard for NRUs, handling ultra-low temperatures (-320°F) and high pressures (up to 2000 psig).
- Design Tip: Prevent fouling with robust upstream filtration and strainers to maintain heat transfer efficiency and avoid pressure drop issues.
- Reflux System:
- A robust reflux system minimizes methane emissions in the nitrogen vent stream (<1 mol% methane). It includes centrifugal pumps, a condenser, and an accumulator to stabilize flow and enhance separation.
- Design Tip: Two cryogenic pump designs are available, mechanical seal and sealless , and both are suitable for use in this design. Communication with the vendor is critical to understand the delivery, setup and utility requirements for each one.
- Compression:
- Feed pressure drives the JT effect for cooling and in some instances inlet compression, or pressure, needs to be optimized to ensure an efficient operation.. Simplifying the compression design and services(feed boost and recompression) enhances reliability.
- Design Tip: Conduct a Reliability, Availability, and Maintainability (RAM) study to optimize compressor performance, as 40% of NRU issues are compression-related.
Strategic Placement for Cryogenic NRUs
NRUs can be placed downstream of NGL extraction plants to process high-methane residue gas, leveraging existing compression for the JT effect. For greenfield projects, integrating NRUs with NGL plants can optimize energy use, though this is less common in mature markets like the US.
Key Takeaways for Cryogenic NRUs
- Single column NRUs suit high-nitrogen, low-capacity operations, while a dual column design excels for efficiency in lower-nitrogen scenarios.
- Robust BAHE and reflux system designs are critical for performance and emissions control.
- Simplified compression and strategic placement enhance NRU operability and cost-effectiveness.
Our final blog will cover NRU fabrication, installation, and startup best practices to ensure smooth operations.
Plan an introduction meeting today
Contact our experts today to discover how our innovative solutions can tackle your complex energy challenges